Table of Contents
Introduction
Restaurants and hospitality businesses operate in an environment where margins stay tight, and competition stays intense. Decisions around pricing, staffing, locations, suppliers, and marketing rely on accurate information. A restaurant and hospitality business database brings scattered data into one structured system that can be controlled.
However, traditional methods of data management, such as spreadsheets or manual record-keeping, are often inadequate for handling the complexities of a modern restaurant or hotel. These methods are prone to errors, lack scalability, and make it difficult to extract meaningful insights from the data.
This guide explains what a restaurant and hospitality business database is, why it matters, and how it supports operations, marketing, analysis, and growth. It also outlines how tools like Outscraper can be used to build and enrich high-quality databases for research, lead generation, and strategic decision-making.
What is a Restaurant and Hospitality Business Database?
A restaurant and hospitality business database is a structured collection of information related to businesses operating within the restaurant, food service, and hospitality sectors. This data is organized in a way that allows for effective searching, filtering, and analysis.
The database can be used for different purposes, including market research, lead generation, competitive analysis, and operational improvement. Recent analysis reveals that poor data management can cost businesses up to 25% of their revenue, undermining the importance of effective information systems in operations and improving profitability.
These databases typically contain a wide range of information that includes;
Basic Business Information:
- Business Name
- Address
- Phone Number
- Email Address
- Website URL
Business Classification:
- Industry Sector (e.g., Restaurant, Hotel, Catering)
- Cuisine Type (e.g., Italian, Mexican, Seafood)
- Restaurant Type (e.g., Fine Dining, Fast Food, Casual Dining)
- Hotel Type (e.g., Luxury, Boutique, Budget)
Operational Details:
- Number of Employees
- Seating Capacity
- Operating Hours
- Services Offered (e.g., Delivery, Takeout, Catering)
- Payment Methods Accepted
- Financial Information (Often Estimated or Publicly Available):
- Annual Revenue
- Profitability
- Investment History
Management and Ownership:
- Owner Name(s)
- Manager Name(s)
- Contact Information for Key Personnel
Marketing and Social Media Presence:
- Social Media Links
- Online Reviews and Ratings
- Marketing Campaigns
Geographic Information:
- Latitude and Longitude
- Neighborhood
- Market Area
Equipment and Supplier Information:
- Suppliers Used
- Equipment Brands
- Technology Solutions
Benefits of Using a Restaurant and Hospitality Business Database
The importance of a restaurant and hospitality business database lies in its value in improving operations, enriching the customer experience, driving targeted marketing efforts, increasing profitability, and promoting sustainable growth.
Improving Operations
A robust database is the backbone of efficient operations in the restaurant and hospitality sector. It serves as a centralized database for critical information, enabling coordination across departments and functions.
- Inventory Management: A database enables real-time tracking of inventory levels, minimizing waste, preventing stockouts, and optimizing ordering processes. By monitoring consumption patterns and identifying popular items, businesses can make informed decisions about purchasing and menu planning.
- Staff Scheduling: Efficient staff scheduling is crucial for managing labor costs and ensuring adequate coverage during peak hours. A database can store employee information, availability, skills, and performance data, facilitating the creation of optimized schedules that meet business needs while considering employee preferences.
- Order Management: For restaurants offering online ordering or delivery services, a database is essential for managing orders, tracking delivery status, and processing payments. It can also integrate with kitchen display systems for order preparation and minimize errors.
- Table Management: For restaurants with table service, a database can be used to manage reservations, track table availability, and optimize seating arrangements. This helps to minimize wait times, improve customer satisfaction, and maximize table turnover.
- Vendor Management: A database can store information about suppliers, including contact details, pricing, and delivery schedules. This allows businesses to easily compare prices, negotiate better deals, and manage vendor relationships effectively.
Enriching Customer Experiences
In the hospitality industry, customer experience is everything. A well-designed database can play a significant role in personalizing interactions, anticipating customer needs, and fostering loyalty.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): A database can serve as a CRM system, storing customer information such as contact details, preferences, order history, and feedback. This allows businesses to personalize marketing campaigns, offer targeted promotions, and provide exceptional customer service.
- Loyalty Programs: A database is essential for managing loyalty programs, tracking customer points, and rewarding loyal customers with exclusive benefits. This encourages repeat business and strengthens customer relationships.
- Personalized Recommendations: By analyzing customer data, businesses can identify patterns and preferences, enabling them to offer personalized recommendations for menu items, drinks, or services. This enhances the customer experience and increases sales.
- Feedback Management: A database can be used to collect and analyze customer feedback, allowing businesses to identify areas for improvement and address customer concerns promptly. This demonstrates a commitment to customer satisfaction and fosters loyalty.
- Special Occasion Recognition: A database can store information about customer birthdays, anniversaries, and other special occasions, allowing businesses to send personalized greetings and offers, creating a memorable experience.
Driving Targeted Marketing Efforts
A database provides valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences, enabling businesses to develop targeted marketing campaigns that are more effective and efficient.
- Segmentation: A database allows businesses to segment their customer base based on demographics, purchase history, preferences, and other criteria. This enables them to tailor marketing messages to specific groups of customers, increasing the likelihood of engagement and conversion.
- Email Marketing: A database can be integrated with email marketing platforms to send targeted emails to customers, promoting new menu items, special events, or exclusive offers.
- Social Media Marketing: A database can be used to identify customers who are active on social media, allowing businesses to target them with relevant ads and content.
- Direct Mail Marketing: For businesses that still use direct mail, a database can be used to create targeted mailing lists, ensuring that marketing materials are sent to the most relevant recipients.
- Performance Tracking: A database allows businesses to track the performance of their marketing campaigns, measuring metrics such as open rates, click-through rates, and conversion rates. This enables them to optimize their campaigns and improve their return on investment.
Increasing Profitability and Promoting Sustainable Growth
By streamlining operations, enhancing customer experiences, and driving targeted marketing efforts, a restaurant and hospitality business database ultimately contributes to increased profitability and sustainable growth.
- Reduced Costs: Efficient inventory management, optimized staff scheduling, and streamlined order processing can all lead to significant cost savings.
- Increased Revenue: Personalized recommendations, targeted marketing campaigns, and loyalty programs can all drive increased sales and revenue.
- Improved Customer Retention: Exceptional customer service, personalized experiences, and loyalty programs can all help to retain customers and build long-term relationships.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: A database provides valuable insights into business performance, allowing managers to make informed decisions about pricing, menu planning, marketing, and operations.
- Competitive Advantage: Businesses that effectively leverage data to improve their operations and customer experiences gain a significant competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Outscraper Database Acquisition
How to acquire a restaurant and hospitality database? The answer is that using a powerful data extraction tool, such as Outscraper, it is used to extract the business data and enrich it with additional information that adds more value to the database. There are simple steps in acquiring these insights:
Step 1: Choose Your Scraper
Create an Outscraper account and select the services that match your goals, such as Google Maps business data or review scraping. Free-tier accounts include limited requests, while pay-as-you-go pricing allows flexible scaling without contracts or recurring fees.
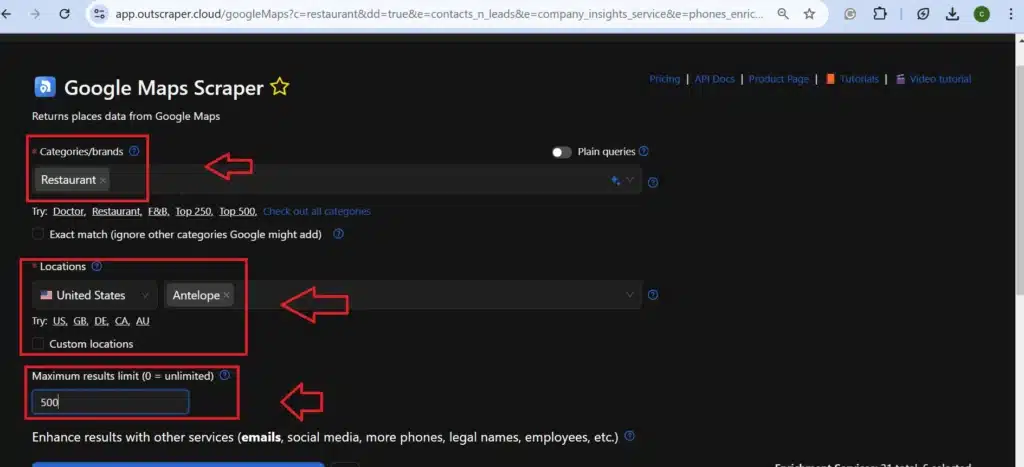
Step 2: Specify Your Scope (Select Filters)
Once you’ve chosen your scraper, you need to define the scope of your data extraction. This involves specifying the search criteria and filters that will be used to identify relevant businesses.
- Categories/ Brands: Use relevant keywords to target specific types of restaurants and hospitality businesses. For example, you could use keywords like “Italian restaurant,” “hotel,” “bed and breakfast,” or “conference center.”
- Location: Specify the geographic location you want to target. This could be a city, region, or specific address.
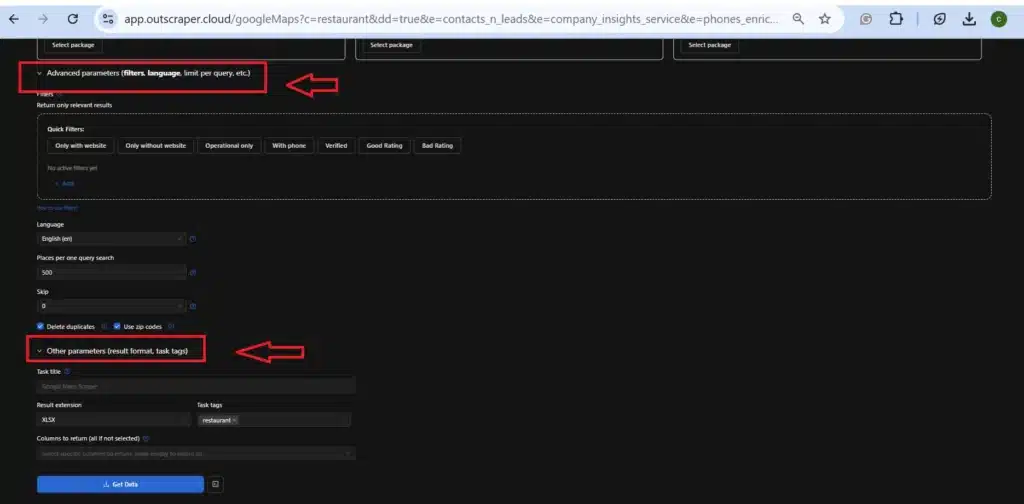
- Filters: Apply filters to narrow down your search results. Advanced parameters (filters, language, limit per query, etc.) and other parameters (result format, task tags).
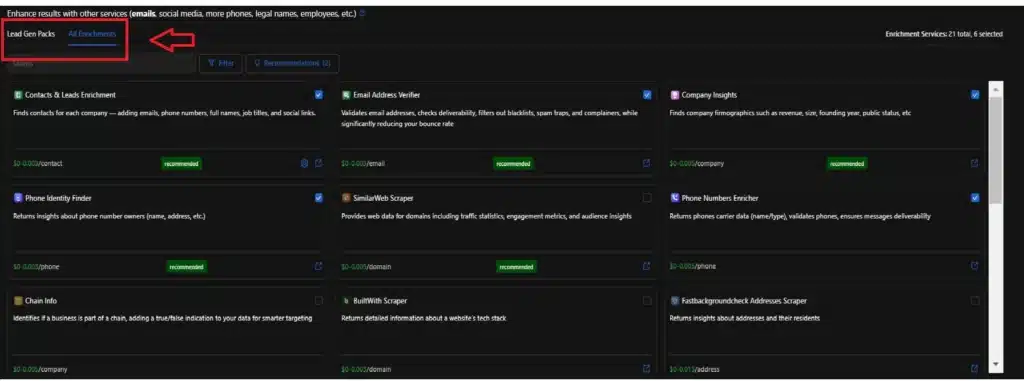
Step 3: Add Enrichments
Outscraper offers a range of data enrichment options that can add significant value to your database. Enrichments involve supplementing the extracted data with additional information from other sources.
By adding enrichments, you can create a more comprehensive and insightful database that provides a deeper understanding of the restaurant and hospitality landscape.
Step 4: Export and Use the Data
After reviewing estimated volume and processing time, data can be exported in multiple formats, including XLSX, CSV, JSON, and Parquet, making it easy to integrate with analytics tools, CRMs, or internal systems.
Use Cases
- Market Research: Understand market trends, identify growth opportunities, and analyze competitor strategies.
- Lead Generation: Identify potential customers for your products or services (e.g., food suppliers, equipment vendors).
- Competitive Analysis: Monitor competitors’ performance, pricing, and marketing efforts.
- Site Selection: Identify optimal locations for new restaurants or hotels based on demographics, competition, and traffic patterns.
- Investment Analysis: Evaluate the financial health and growth potential of restaurant and hospitality businesses.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Identify and connect with suppliers of food, equipment, and other essential resources.
- Sales and Marketing: Target specific segments of the industry with tailored marketing campaigns.
- Operational Improvement: Benchmark performance against industry averages and identify areas for improvement.
- Risk Management: Assess the financial stability of potential partners or clients.
Conclusion
Restaurant and hospitality businesses depend on accurate, structured data to operate, compete, and grow. The article shows how a centralized database replaces fragmented spreadsheets and manual tracking with a system that supports operations, customer experience, marketing, and profitability. Inventory control, staff scheduling, vendor management, and customer engagement all improve when decisions rely on reliable data rather than assumptions.
A well-built database also supports targeted marketing, competitive analysis, site selection, and risk management. By organizing business details, operational metrics, customer behavior, and market signals, operators gain visibility across the entire business. This leads to better cost control, stronger customer retention, and data-driven planning.
Outscraper supports this process by extracting restaurant and hospitality business data at scale and enriching it with verified contacts, reviews, store locations, and more. With flexible filters, enrichment options, and multiple export formats, use Outscraper that enables businesses, analysts, and marketers to build a usable database without long-term contracts or manual collection. In attaining the goal of gaining accurate market insight, strengthening operations, and relying on dependable data, Outscraper provides the foundation to build and maintain a high-quality restaurant and hospitality business database.
FAQ
Most frequent questions and answers
A Restaurant and Hospitality Business Database is a specialized dataset compiling detailed information on restaurants, hotels, and related hospitality venues for B2B purposes like lead generation and market analysis.
Location intelligence refers to the process of analyzing geospatial data, such as maps, demographics, traffic patterns, and points of interest, to derive actionable business insights.
Verified contact information refers to contact details like email addresses, phone numbers, or physical addresses that have been confirmed as accurate and belonging to the intended person or business through validation processes.
Reputation management involves monitoring, influencing, and maintaining a positive public image for individuals, businesses, or brands, particularly online.
Sentiment analysis determines the emotional tone behind text data, classifying it as positive, negative, or neutral. Businesses apply it to customer feedback, social media, and reviews to gauge opinions and detect trends
Negative reviews signal customer dissatisfaction but can also enhance authenticity and drive sales from discerning buyers. They impact revenue by deterring impulse purchases while offering opportunities for improvement and engagement.
Qualifying opportunities from negative reviews involves scraping feedback for pain points, prioritizing high-intent signals like recent complaints, and personalizing outreach to convert dissatisfied businesses into leads.
Google Maps serves as a public mapping platform providing geospatial data on businesses, landmarks, and properties, including user-generated details like photos, reviews, and contact information, which supports lead generation in digital marketing
A retail store is a business establishment where goods or services are sold directly to individual consumers for personal use. Toggle Content